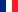
Infrared radiation is applied for…
- Heating
- Welding
- Soldering
- Sintering
- Tempering
- Drying
- Evaporation
- Dehydration
- Adhesives
- Fixation
- Drying
- Activation
- Curing
- Thermoforming
- Blow Molding
- Deep Drawing
- Foaming
- Imprinting
- Shrinking
- Concealing
- Vulcanization
- Lamination
Infrared Radiation...
- has due to the specific features.a varied and individual range of applications.
- depending on the wave length of the light can be divided into long-wave, medium-wave, fast response medium-wave, short-wave and near-UV infrared.
- used in countless applications in Plastics-,Chemical-, Printing-, Wood-, Metal-, Paper-, Textile-, Food- and Automotive Industries.
- can be absorbed directly, reflected or transmitted through the body. All this depending upon the material’s nature. That’s why it is essentially important to find out the optimal emitter type for your specific heating purpose.
- and temperature gradients produce a controllable energy output, adjusted to match the heating requirements.
- the heating modules as well as the controlling and measuring technique are optimally designed. This guarantees optimum efficiency and quality.
- offers a wide range of possibilities to match temperature profiles with customer’s needs. The heat region zoning saves energy and money.
Provides following benefits…
- the process is economical and allows highly efficient heating processes.
- is a clean electrical heat source.
- is fast and immediately ready to use.
- is compact and has a small footprint.
- high heating up rates, due to the large power densities.
- an individually shaped and targeted heat section.
- requires no contact with the material.
- repeatable results can be achieved for consistent process outputs.
The emitter wavelength.....
- is customized for industrial applications.The diagram on the left shows the most productive wavelength coverage of 1 – 4 µm.
- and the different designs and burning temperatures of the heating filament on infrared emitters.
- Medium Wave Infrared Emitters: Filament temperature: approx. 850 °C Emissions maximum: 2,0-2,6 µm
- Star Shape Infrared Emitters: Filament temperature: up to 1400°C Emissions maximum: 1,8-2,2 µm
- Fast Medium Wave Infrared Emitters: Filament temperature: up to 1600 °C Emissions maximum: 1,4-1,9 µm (Filament in Star Shape design)
- Short Wave Emitters (double tube/twin tube): Filament temperature: up to 2100 °C Emissions maximum: 0,9-1,6 µm Short Wave Emitters (single tube): Filament temperature: above 2500 °C Emissions maximum: 0,8-1,6 µm
Heating up of plastic by infrared...... During the heating up process it should be considered that…
- only the appropriate emitter type achieves efficient and economically advantages.
- Absorption-Diagram on the right shows: Material: Polyethylene 0,1 mm As lined purple Material: PVC 0,02 mm As lined blue Wave length range: 1 – 4 µm Substantial effect of the infrared emitter: 3,2 – 3,8 µm.
- physically seen, the emission behavior should,as accurately as, match the absorption behavior. The diagram shows that the directly usable portions of the radiating power obtain a higher efficiency if the emission maximum of an infrared emitter is as congruent as possible with the curves represented in purple or in blue.
- the red curve represents short wave emitters, in light blue is drawn the spectrum Star Shape emitters and the dark blue curve shows medium wave emitter types.
Drying water-based paint by infrared…… During the drying process it should be considered that…
- only the appropriate emitter type achieves efficient and economically advantages.
- Absorption Diagram on the left shows: Water, as lined aquamarine.Wave length range: 1 – 4 µm Substantial effect of the infrared emitter: 2,5 – 3,5µm
- physically seen, the emission behavior should,as accurately as, match the absorption behavior. The diagram shows that the directly usable portions of the radiating power obtain a higher efficiency if the emission maximum of an infrared emitter is as congruent as possible with the in aquamarine represented curve.
- the red curve represents short wave emitters, in light blue is drawn the spectrum Star Shape emitters and the dark blue curve shows medium wave emitter types.